Income statements can be created to analyze and compare business performance over a month, a quarter or a year, and are an effective tool to review cash flow and predict future business performance. Use our free income statement template to review your business performance, and check out the Wise multi-currency account as a smart way to cut your bank charges. An accounting system that doesn’t record accruals but instead recognizes income only when payment is received and expenses only when payment is made. There’s no match of revenue against expenses in a fixed accounting period, so comparisons of previous periods aren’t possible. Gross profit margin is the difference between revenue and cost of goods. Gross profit margin can be expressed in dollars, as a percentage, or both.
Income statement vs balance sheet
Both the income statement and balance sheet are important financial statements – but each has a different function for business owners and investors.
A balance sheet gives a point in time view of a company’s assets and liabilities, while the income statement details income and expenses over an extended period of time (usually one year). A balance sheet helps determine a company’s current financial situation and make important financial decisions. The income statement can be run at any time of the fiscal year to determine profitability and compare one period of time to another to show growth.
A customer may take goods/services from a company on Sept. 28, which will lead to the revenue accounted for in September. The customer may be given a 30-day payment window due to his excellent credit and reputation, allowing until Oct. 28 to make the payment, which is when the receipts are accounted for. With a Wise Business account you can keep multiple currencies in one account. Save time, cut costs, and connect with more customers all over the world, with Wise. Are you invoicing clients overseas, or working with suppliers based abroad, but waiting around for slow international transfers to finally reach your account? Wise can cut down on the cost and time of international transfers into your multi-currency account.
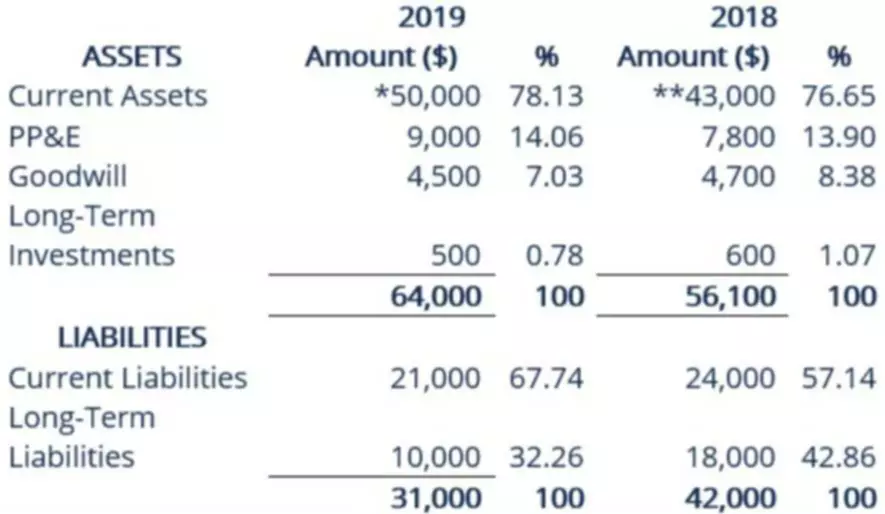
A Real Example of an Income Statement
income statements are often shared as quarterly and annual reports, showing financial trends and comparisons over time. An income statement is a rich source of information about the key factors responsible for a company’s profitability. It gives you timely updates because it is generated much more frequently than any other statement. The income statement shows a company’s expense, income, gains, and losses, which can be put into a mathematical equation to arrive at the net profit or loss for that time period. This information helps you make timely decisions to make sure that your business is on a good financial footing.

Also sometimes referred to as “operating expenses,” these include rent, bank & ATM fee expenses, equipment expenses, marketing & advertising expenses, merchant fees, and any other expenses you need to make to keep your business going. Consider enrolling in Financial Accounting or our other online finance and accounting courses, which can teach you the key financial topics you need to understand business performance and potential. Download our free course flowchart to determine which best aligns with your goals. Because of this, horizontal analysis is important to investors and analysts. By conducting a horizontal analysis, you can tell what’s been driving an organization’s financial performance over the years and spot trends and growth patterns, line item by line item.
Net profit
After deducting all the above expenses, we finally arrive at the first subtotal on the income statement, Operating Income . It is common for companies to split out interest expense and interest income as a separate line item in the income statement. This is done in order to reconcile the difference between EBIT and EBT. Net income after taxes is an accounting term most often found in an annual report, and used to show the company’s definitive bottom line.
We specialize in unifying and optimizing processes to deliver a real-time and accurate view of your financial position. ExpensesAn expense is a cost incurred in completing any transaction by an organization, leading to either revenue generation creation of the asset, change in liability, or raising capital. Amount of income related to nonoperating activities, classified as other.
Profit Before Tax
It is called the bottom line of the income statement as it represents the final result of the business activities. An analyst should identify differences in companies’ expense recognition methods and adjust reported financial statements where possible to facilitate comparability. Also sometimes called a “net income statement” or a “statement of earnings,” the income statement is one of the three most important financial statements in financial accounting, along with the balance sheet and the cash flow statement . The Income Statement is one of a company’s core financial statements that shows their profit and loss over a period of time.
These are all expenses that go toward a loss-making sale of long-term assets, one-time or any other unusual costs, or expenses toward lawsuits. A business’s cost to continue operating and turning a profit is known as an expense.
Generally, they show revenue minus expenses and losses to give a company’s profit or loss over that time period. https://www.bookstime.com/s are one of several documents you’ll want to look at if you are considering investing in a stock in addition to balance sheets and cash flow statements.
What is in an income statement?
An income statement shows a company's revenues, expenses and profitability over a period of time. It is also sometimes called a profit-and-loss (P&L) statement or an earnings statement. It shows your: revenue from selling products or services. expenses to generate the revenue and manage your business.
But taking the time to learn about financial statements, such as an income statement, can go far in helping you advance your career. Cumulative effect of changes in accounting policies is the difference between the book value of the affected assets under the old policy and what the book value would have been if the new principle had been applied in the prior periods. For example, valuation of inventories using LIFO instead of weighted average method. The changes should be applied retrospectively and shown as adjustments to the beginning balance of affected components in Equity. The above example is one of the simplest types of income statements, where you apply the values of income, expense, gains and loss into the equation to arrive at the net income.